A guide to practicing Open Science with Sysrev Part 3: A real-world example
In part 1 and part 2 of this guide, we discussed best practices for data sharing and reuse with Sysrev. In part 3, we share an example of how Sysrev was used to share the underlying data from a real-world project.
Sharing data from a review of AI usage and reporting in evidence synthesis
Dr. Kristin Scotti and colleagues at Carnegie Mellon University conducted a large-scale methodological review examining the use and reporting of artificial intelligence (AI) and other automation techniques in evidence synthesis. Using Sysrev, the authors screened and extracted data from more than 2,000 systematic and related reviews published by Cochrane, the Campbell Collaboration, and the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence. The primary objective of the review was to characterize how AI and automation have been incorporated into evidence synthesis workflows since 2017, and how these tools are described and reported across different stages of the review process. To support this aim, the authors extracted rich, structured metadata from each included review, capturing both the nature of AI use and the transparency of its reporting. The findings of this work are reported in Cochrane Evidence Synthesis and Methods.
As evidence synthesis methodologists, the authors recognized the importance of methodological transparency and the value of sharing the underlying data that support their analyses. To facilitate openness and reuse, they made their data publicly available via Sysrev. As described in the published article, “A bibliographic file (RIS) of included studies was generated using Zotero and uploaded to a publicly available Sysrev [73] project (https://www.sysrev.com/o/1605/p/199195) for data management” (p. 5). Within the Sysrev project, the authors provide comprehensive contextual information, including a link to the final published review, a complete list of authors, a suggested citation for the dataset, and a data reuse license. They also link to a second Sysrev project that contains the detailed extracted data.
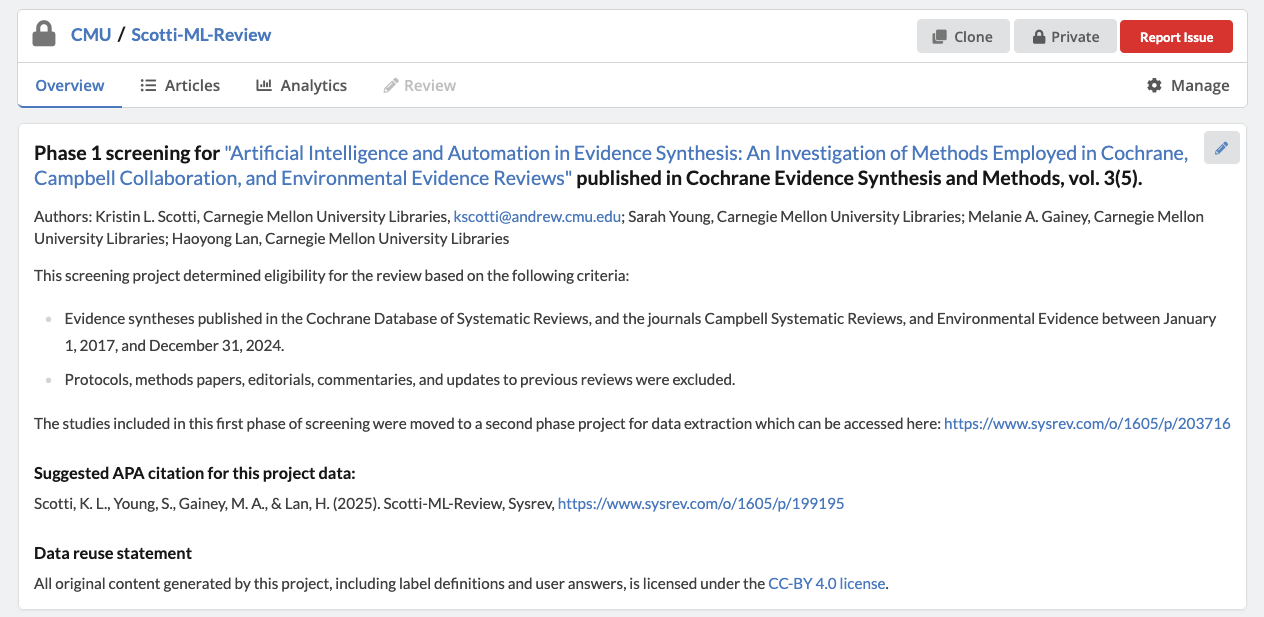
By sharing their Sysrev project, the authors enable other researchers to easily download the complete dataset, reproduce the original analyses, or conduct alternative analyses to generate new insights. In addition, Sysrev’s project cloning functionality allows users to duplicate the original project framework, including the data extraction form. This makes it straightforward for other research teams to extend the investigation to additional reviews, journals, time periods, or disciplines using a directly comparable methodology. In this way, subsequent studies can build cumulatively on the existing evidence base, supporting more robust and comparable research on the use and reporting of AI and automation in evidence synthesis.
Explore more real-world applications of Sysrev
Interested in seeing more examples of published work using Sysrev? Please explore our "research using Sysrev" collection. You can navigate the collection by discipline, study type and whether or not the paper shared a public Sysrev project.
If you'd like to share your own use of Sysrev for highlighting in a future newsletter or webinar, please get in touch at support@sysrev.com! We'd love to hear from you.
